Energy-Based Models for Deep Probabilistic Regression
Abstract
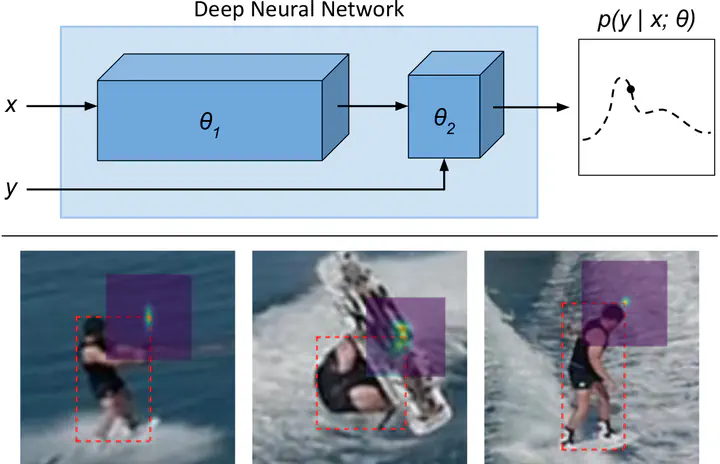
While deep learning-based classification is generally tackled using standardized approaches, a wide variety of techniques are employed for regression. In computer vision, one particularly popular such technique is that of confidence-based regression, which entails predicting a confidence value for each input-target pair (x,y). While this approach has demonstrated impressive results, it requires important task-dependent design choices, and the predicted confidences lack a natural probabilistic meaning. We address these issues by proposing a general and conceptually simple regression method with a clear probabilistic interpretation. In our proposed approach, we create an energy-based model of the conditional target density p(y|x), using a deep neural network to predict the un-normalized density from (x,y). This model of p(y|x) is trained by directly minimizing the associated negative log-likelihood, approximated using Monte Carlo sampling. We perform comprehensive experiments on four computer vision regression tasks. Our approach outperforms direct regression, as well as other probabilistic and confidence-based methods. Notably, our model achieves a 2.2% AP improvement over Faster-RCNN for object detection on the COCO dataset, and sets a new state-of-the-art on visual tracking when applied for bounding box estimation. In contrast to confidence-based methods, our approach is also shown to be directly applicable to more general tasks such as age and head-pose estimation.